As automotive electronics are getting more and more complex, automotive manufacturers have been seeking more streamlined and efficient methods of integrating the audio system. At first thought, the audio system is simple - it just plays music from the radio, right? Well it also needs to integrate audio from the GPS system, the backup sensors, Bluetooth integration, in-car entertainment, and any other number of devices. Integrating independent wiring for each device while keeping the size and cost of wiring to a minimum and high enough quality to carry high-quality audio is an engineering challenge.
Systems are added as nodes on a ring
Enter MOST - it is a fiber optic network designed to carry digital signals. In automotive applications, it is generally used to integrate multimedia devices, such as the in-car entertainment system. The fiber-optic cable is arranged in a ring - devices that need to interact with the multimedia system, such as the radio, GPS, or DVD entertainment systems, are added as nodes on the ring. Each device is able to communicate with each other for interactive communication, control, and content transfer.
The center console is plugged into the network
In my Volvo XC90, the radio in the center console is not really a radio - it is just a display unit, button panel, and CD changer. There is no audio amplifier in the center console, but there is a MOST interface. The center console is plugged into the MOST network and is able to communicate with the radio receiver mounted above the headliner in the trunk area.
The radio receiver module also contains the satellite radio receiver and the FM and AM radio receiver. This module only contains the receiver circuitry - no audio processing circuitry is in the radio receiver module. The center console keypad and display interacts with the radio receiver module to control it to tune into the radio stations and satellite radio stations the user wants, and passes the audio signal over the MOST-bus to the audio amplifier.
The amplifier converts the digital signal to analog
The audio amplifier on my XC90 is located under the front passenger seat. There are no analog audio hookups - the only hookups are power and MOST-bus. The audio amplifier receives the decoded audio from either the center console (for CDs or AUX-in) or the radio receiver (for broadcast and satellite radio) and converts the digital signal to an analog signal that can be amplified and played over the speakers.
In this simplified explanation, the benefits allow the engineers to integrate a complete audio entertainment system without complex wiring or additional bulky cabling. However, the downside is it makes the sound system aggravatingly difficult to make changes. In my 2006 XC90, there was no provision for an auxiliary input to allow you to connect a media player or cell phone. Since there are no traditional analog signal paths until the audio amplifier decodes the signal and amplifies it for the speakers, there is no easy way to add an aftermarket aux-in to the audio system. There is also no easy way to upgrade the head-unit without changing a large amount of the integrated electronics.
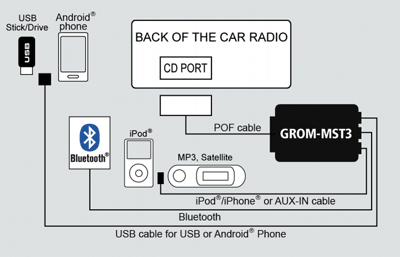
An aux-in interface box for the 2002-2006 Volvo XC90 by Grom Audio
The solution for my 2006 XC90 was to install an aftermarket aux-in box from Grom Audio. Grom Audio, along with several other companies like Dension have reverse-engineered the MOST network on Volvo and many other European vehicles, allowing them to manufacture devices that can interface and add capabilities to the factory MOST network.
Interface diagram of the GROM Audio aux-in interface box for Volvo
It's difficult to add additional functions to many European cars
In my XC90, Grom Audio was able to add the aux-in capability by bypassing and emulating the function of the in-dash 6-CD changer. The installation requires the user to disconnect the MOST cabling from the CD-changer and install the aux-in interface box in the CD changer's place. The aux-in interface box then plays the role of the CD-changer, but allows the user to add an auxiliary input, Bluetooth, and USB capability to the factory radio system.
Hopefully this simplified explanation of MOST-bus used in many European cars provides an easy-to-understand top-level overview of this technology, and also explains just why it is so difficult to add additional functions to many European cars.
Sources:
MOST Cooperation - http://www.mostcooperation.com/
MOST Bus - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MOST_Bus
GROM Audio - http://www.gromaudio.com/
Dension - http://www.dension.com/
What have been your experiences working with European audio systems equipped with MOST-bus?